
Add manually specified locked constraints
Source:R/add_manual_locked_constraints.R
add_manual_locked_constraints.RdAdd constraints to a conservation planning problem to ensure
that solutions allocate (or do not allocate) specific planning units to
specific management zones. This function offers more fine-grained control
than the add_locked_in_constraints() and
add_locked_out_constraints() functions.
Usage
add_manual_locked_constraints(x, data)
# S4 method for class 'ConservationProblem,data.frame'
add_manual_locked_constraints(x, data)
# S4 method for class 'ConservationProblem,tbl_df'
add_manual_locked_constraints(x, data)Arguments
- x
problem()object.- data
data.frameortibble::tibble()object. See the Data format section for more information.
Value
An updated problem() object with the constraints added to it.
Data format
The argument to data should be a data.frame with the following columns:
- pu
integerplanning unit identifiers. Ifxhasdata.frameplanning units, then these values must refer to values in theidcolumn of the planning unit data. Alternatively, ifxhassf::st_sf()ormatrixplanning units, then these values must refer to the row numbers of the planning unit data. Additionally, ifxhasnumericvector planning units, then these values must refer to the element indices of the planning unit data. Finally, ifxhasterra::rast()planning units, then these values must refer to cell indices.- zone
characternames of zones. Note that this argument is optional for arguments toxthat contain a single zone.- status
numericstatus values. These values indicate how much of each planning unit should be allocated to each zone in the solution. For example, thenumericvalues could be binary values (i.e., zero or one) for problems containing binary-type decision variables (using theadd_binary_decisions()function). Alternatively, thenumericvalues could be proportions (e.g., 0.5) for problems containing proportion-type decision variables (using theadd_proportion_decisions()).
See also
See constraints for an overview of all functions for adding constraints.
Other functions for adding constraints:
add_contiguity_constraints(),
add_feature_contiguity_constraints(),
add_linear_constraints(),
add_locked_in_constraints(),
add_locked_out_constraints(),
add_mandatory_allocation_constraints(),
add_manual_bounded_constraints(),
add_neighbor_constraints()
Examples
# \dontrun{
# set seed for reproducibility
set.seed(500)
# load data
sim_pu_polygons <- get_sim_pu_polygons()
sim_features <- get_sim_features()
sim_zones_pu_polygons <- get_sim_zones_pu_polygons()
sim_zones_features <- get_sim_zones_features()
# create minimal problem
p1 <-
problem(sim_pu_polygons, sim_features, "cost") %>%
add_min_set_objective() %>%
add_relative_targets(0.2) %>%
add_binary_decisions() %>%
add_default_solver(verbose = FALSE)
# create problem with locked in constraints using add_locked_constraints
p2 <- p1 %>% add_locked_in_constraints("locked_in")
# create identical problem using add_manual_locked_constraints
locked_data <- data.frame(
pu = which(sim_pu_polygons$locked_in),
status = 1
)
p3 <- p1 %>% add_manual_locked_constraints(locked_data)
# solve problems
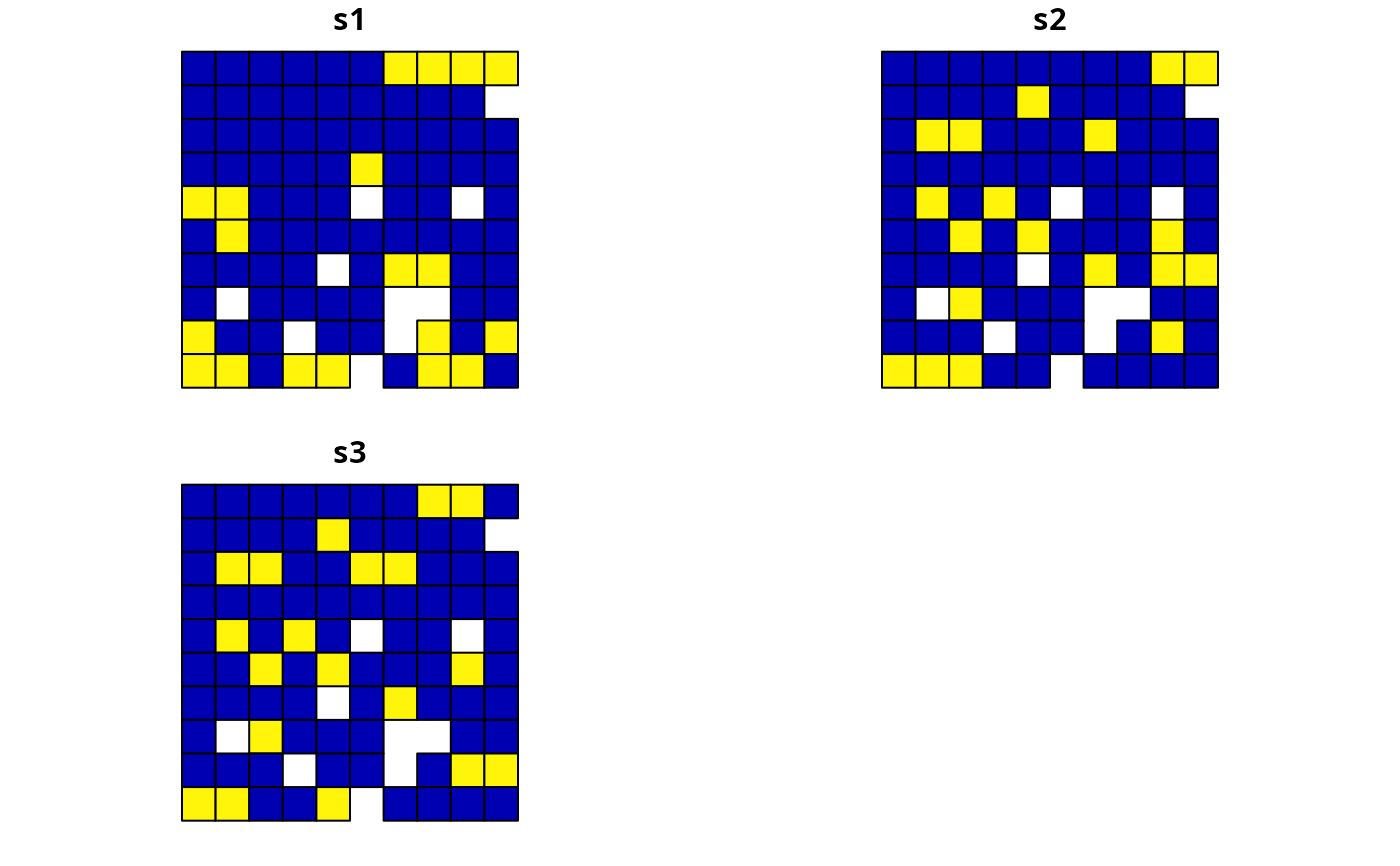
s1 <- solve(p1)
s2 <- solve(p2)
s3 <- solve(p3)
# create object with all solutions
s4 <- sf::st_sf(
tibble::tibble(
s1 = s1$solution_1,
s2 = s2$solution_1,
s3 = s3$solution_1
),
geometry = sf::st_geometry(s1)
)
# plot solutions
## s1 = none locked in
## s2 = locked in constraints
## s3 = manual locked constraints
plot(s4)
 # create minimal problem with multiple zones
p5 <-
problem(
sim_zones_pu_polygons, sim_zones_features,
c("cost_1", "cost_2", "cost_3")
) %>%
add_min_set_objective() %>%
add_relative_targets(matrix(runif(15, 0.1, 0.2), nrow = 5, ncol = 3)) %>%
add_binary_decisions() %>%
add_default_solver(verbose = FALSE)
# create data.frame with the following constraints:
# planning units 1, 2, and 3 must be allocated to zone 1 in the solution
# planning units 4, and 5 must be allocated to zone 2 in the solution
# planning units 8 and 9 must not be allocated to zone 3 in the solution
locked_data2 <- data.frame(
pu = c(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 9),
zone = c(rep("zone_1", 3), rep("zone_2", 2),rep("zone_3", 2)),
status = c(rep(1, 5), rep(0, 2))
)
# print locked constraint data
print(locked_data2)
#> pu zone status
#> 1 1 zone_1 1
#> 2 2 zone_1 1
#> 3 3 zone_1 1
#> 4 4 zone_2 1
#> 5 5 zone_2 1
#> 6 8 zone_3 0
#> 7 9 zone_3 0
# create problem with added constraints
p6 <- p5 %>% add_manual_locked_constraints(locked_data2)
# solve problem
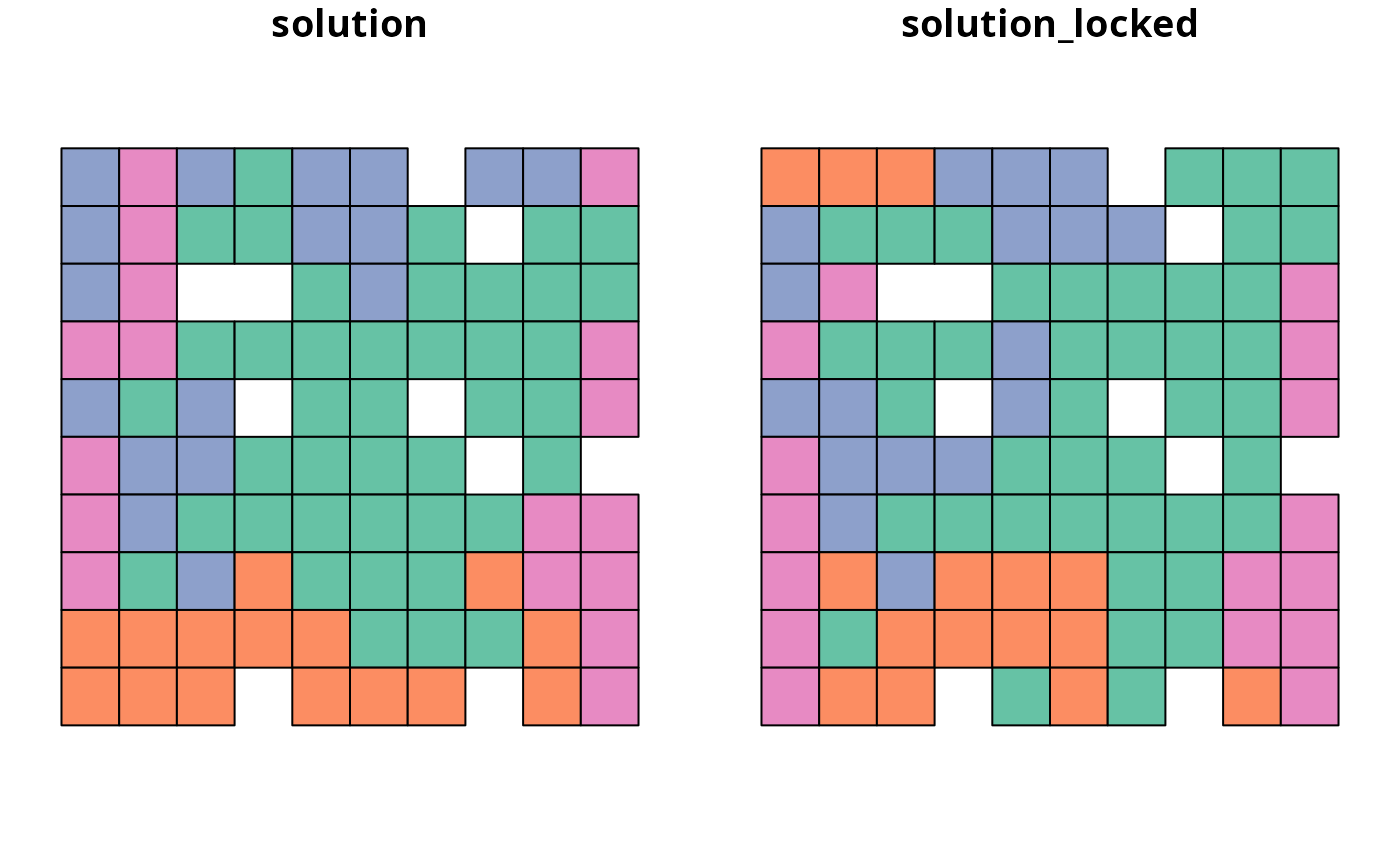
s5 <- solve(p5)
s6 <- solve(p6)
# create two new columns representing the zone id that each planning unit
# was allocated to in the two solutions
s5$solution <- category_vector(sf::st_drop_geometry(
s5[, c("solution_1_zone_1", "solution_1_zone_2", "solution_1_zone_3")]
))
s5$solution <- factor(s5$solution)
s5$solution_locked <- category_vector(sf::st_drop_geometry(
s6[, c("solution_1_zone_1", "solution_1_zone_2", "solution_1_zone_3")]
))
s5$solution_locked <- factor(s5$solution_locked)
# plot solutions
plot(s5[, c("solution", "solution_locked")], axes = FALSE)
# create minimal problem with multiple zones
p5 <-
problem(
sim_zones_pu_polygons, sim_zones_features,
c("cost_1", "cost_2", "cost_3")
) %>%
add_min_set_objective() %>%
add_relative_targets(matrix(runif(15, 0.1, 0.2), nrow = 5, ncol = 3)) %>%
add_binary_decisions() %>%
add_default_solver(verbose = FALSE)
# create data.frame with the following constraints:
# planning units 1, 2, and 3 must be allocated to zone 1 in the solution
# planning units 4, and 5 must be allocated to zone 2 in the solution
# planning units 8 and 9 must not be allocated to zone 3 in the solution
locked_data2 <- data.frame(
pu = c(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 9),
zone = c(rep("zone_1", 3), rep("zone_2", 2),rep("zone_3", 2)),
status = c(rep(1, 5), rep(0, 2))
)
# print locked constraint data
print(locked_data2)
#> pu zone status
#> 1 1 zone_1 1
#> 2 2 zone_1 1
#> 3 3 zone_1 1
#> 4 4 zone_2 1
#> 5 5 zone_2 1
#> 6 8 zone_3 0
#> 7 9 zone_3 0
# create problem with added constraints
p6 <- p5 %>% add_manual_locked_constraints(locked_data2)
# solve problem
s5 <- solve(p5)
s6 <- solve(p6)
# create two new columns representing the zone id that each planning unit
# was allocated to in the two solutions
s5$solution <- category_vector(sf::st_drop_geometry(
s5[, c("solution_1_zone_1", "solution_1_zone_2", "solution_1_zone_3")]
))
s5$solution <- factor(s5$solution)
s5$solution_locked <- category_vector(sf::st_drop_geometry(
s6[, c("solution_1_zone_1", "solution_1_zone_2", "solution_1_zone_3")]
))
s5$solution_locked <- factor(s5$solution_locked)
# plot solutions
plot(s5[, c("solution", "solution_locked")], axes = FALSE)
 # }
# }