An objective is used to specify the overall goal of a conservation planning problem. All conservation planning problems involve minimizing or maximizing some kind of objective. For instance, the planner may require a solution that conserves enough habitat for each species while minimizing the overall cost of the reserve network. Alternatively, the planner may require a solution that maximizes the number of conserved species while ensuring that the cost of the reserve network does not exceed the budget. Please note that all conservation planning problems require an objective function, and attempting to solve a problem without an objective will result in an error.
Details
The following functions can be used to add an objective to a
conservation planning problem().
For the vast majority of conservation planning exercises,
the minimum set and minimum shortfall objectives are most appropriate.
Note that if multiple
of these functions are added to a problem(), then only the last
function added will be used.
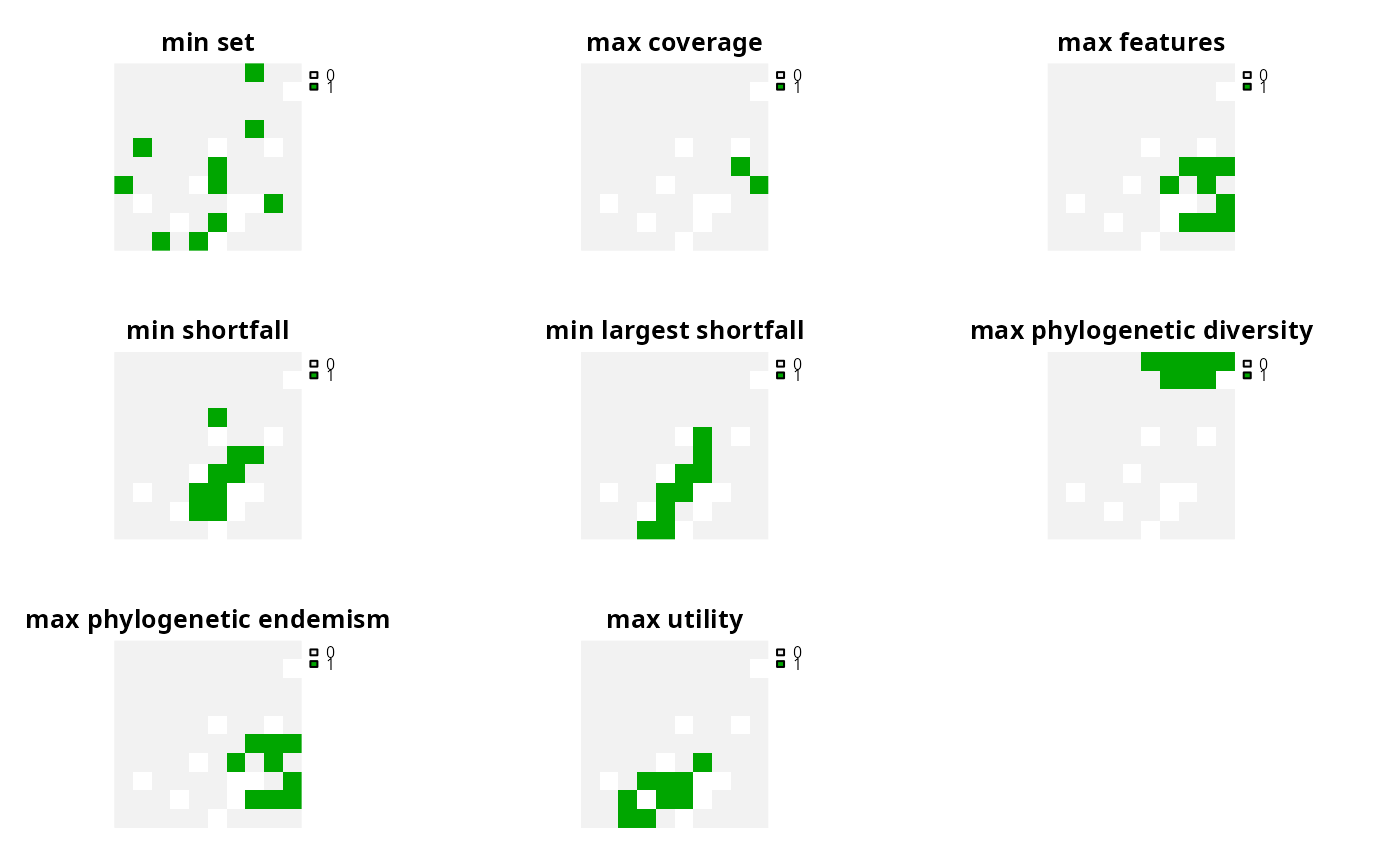
add_min_set_objective()Minimize the cost of the solution whilst ensuring that all targets are met. This objective is similar to that used in Marxan.
add_min_shortfall_objective()Minimize the overall (weighted sum) shortfall for as many targets as possible while ensuring that the cost of the solution does not exceed a budget.
add_min_penalties_objective()Minimize the penalties associated with a problem as much as possible subject to a budget. This is mainly used when performing hierarchical multi-objective optimization.
add_min_largest_shortfall_objective()Minimize the largest (maximum) shortfall among all targets while ensuring that the cost of the solution does not exceed a budget.
add_max_phylo_div_objective()Maximize the phylogenetic diversity of the features represented in the solution subject to a budget.
add_max_phylo_end_objective()Maximize the phylogenetic endemism of the features represented in the solution subject to a budget.
add_max_features_objective()Fulfill as many targets as possible while ensuring that the cost of the solution does not exceed a budget.
add_max_cover_objective()Represent at least one instance of as many features as possible within a given budget. Note that this objective is not compatible with targets.
add_max_utility_objective()Maximize the weighted sum of the features represented by the solution subject to a budget. Note that this objective is not compatible with targets.
See also
Other overviews:
constraints,
decisions,
importance,
penalties,
portfolios,
solvers,
summaries,
targets
Examples
# \dontrun{
# load data
sim_pu_raster <- get_sim_pu_raster()
sim_features <- get_sim_features()
sim_phylogeny <- get_sim_phylogeny()
# create base problem
p <-
problem(sim_pu_raster, sim_features) %>%
add_relative_targets(0.1) %>%
add_binary_decisions() %>%
add_default_solver(verbose = FALSE)
# create problem with added minimum set objective
p1 <- p %>% add_min_set_objective()
# create problem with added maximum coverage objective
# note that this objective does not use targets
p2 <- p %>% add_max_cover_objective(500)
# create problem with added maximum feature representation objective
p3 <- p %>% add_max_features_objective(1900)
# create problem with added minimum shortfall objective
p4 <- p %>% add_min_shortfall_objective(1900)
# create problem with added minimum largest shortfall objective
p5 <- p %>% add_min_largest_shortfall_objective(1900)
# create problem with added maximum phylogenetic diversity objective
p6 <- p %>% add_max_phylo_div_objective(1900, sim_phylogeny)
# create problem with added maximum phylogenetic diversity objective
p7 <- p %>% add_max_phylo_end_objective(1900, sim_phylogeny)
# create problem with added maximum utility objective
# note that this objective does not use targets
p8 <- p %>% add_max_utility_objective(1900)
# solve problems
s <- c(
solve(p1), solve(p2), solve(p3), solve(p4), solve(p5), solve(p6),
solve(p7), solve(p8)
)
#> Warning: `problem()` has an objective that does not support targets.
#> ℹ The specified targets will be ignored during optimization.
#> ℹ If the targets are important, then use a different objective.
#> Warning: `problem()` has an objective that does not support targets.
#> ℹ The specified targets will be ignored during optimization.
#> ℹ If the targets are important, then use a different objective.
names(s) <- c(
"min set", "max coverage", "max features", "min shortfall",
"min largest shortfall", "max phylogenetic diversity",
"max phylogenetic endemism", "max utility"
)
# plot solutions
plot(s, axes = FALSE)
 # }
# }
